-
Products
- Superflexible Foam Dielectric RF Cables
- Low Loss Foam Dielectric RF Cables
- Aluminium Foam Dielectric RF Cables
- Low Loss High Power Air Dielectric RF Cables
- Radiating Cables
- Superflexible Jumper Cable Assemblies Size 1/4
- Superflexible Jumper Cable Assemblies Size 3/8
- Superflexible Jumper Cable Assemblies Size 1/2
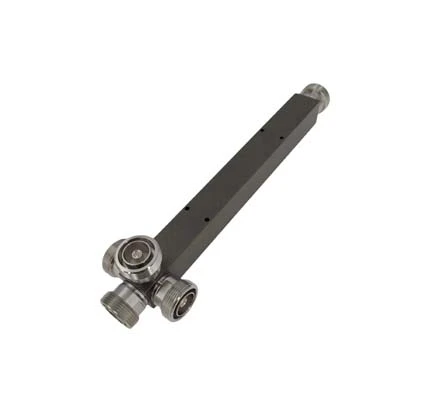
- Power Splitters
- Directional Couplers
- Power Tappers
- Hybrid Couplers
- RF Attenuators
- Dummy Loads
- Multi-Input Multi-Output Combiner, 900/1800/2100/2600MHz, Used for Passive DAS Deployment
- Multi-Operator POI, 800/900/1800MHz, 19'' Rack Mounting, N Female
- IBS Multi-Input Combiner Unit, 24-Port, MIMO Application
- DAS Combiner Unit, 900/1800/2300MHz, Indoor Coverage, Wall Mounting
- C-DAS Combiner, Sharing DAS, 1800/2300/2600MHz
- Indoor System Combiner Matrix Unit, Rack Mounting, 8-Port
- SuperFlexible Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, 1/4 in, Black PE Jacket
- SuperFlexible Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, 1/4 in, Non-Halogenated and Fire Retardant (LSZH) Jacket
- SuperFlexible Foam Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, 3/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- SuperFlexible Foam Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, 3/8 in, Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive (FRNC) Jacket
- SuperFlexible RF Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, 1/2 in, Black PE Jacket
- SuperFlexible RF Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, 1/2 in, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Jacket
- Foam Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper Tube, CCA Wire, 1/4 in, Black PE Jacket
- Foam Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper Tube, CCA Wire, 1/4 in, Non-Halogenated and Fire Retardant (LSZH) Jacket
- RF Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, Copper-Clad-Aluminum Wire, 3/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- RF Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Copper, Copper-Clad-Aluminum Wire, 3/8 in, Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive (FRNC) Jacket
- Foam Coaxial Feeder Cable, Corrugated Copper, 1/2 in, Black PE Jacket
- Foam Coaxial Feeder Cable, Corrugated Copper, 1/2 in, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Jacket
- RF Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Aluminum, 7/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- RF Coaxial Cable, Corrugated Aluminum, 7/8 in, Non-Halogenated And Fire Retardant (LSZH) Jacket
- Foam Coaxial Aluminum Cable, Corrugated Aluminum, 1-1/4 in, Black PE Jacket
- Foam Coaxial Aluminum Cable, Corrugated Aluminum, 1-1/4 in, Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive (FRNC) Jacket
- Aluminum Coaxial RF Cable, Corrugated Aluminum, 1-5/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- Aluminum Coaxial RF Cable, Corrugated Aluminum, 1-5/8 in, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Jacket
- Air Dielectric Coaxial Cable 50 Ohm, Corrugated Copper, 5/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- Air Dielectric Coaxial Cable 50 Ohm, Corrugated Copper, 5/8 in, Non-Halogenated And Fire Retardant (LSZH) Jacket
- Dielectric Coaxial RF Air Cable 50 Ohm, Corrugated Copper, 7/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- Dielectric Coaxial RF Air Cable 50 Ohm, Corrugated Copper, 7/8 in, Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive (FRNC) Jacket
- Air Insulated Coaxial Cable 50 Ohm, Corrugated Copper, 1-5/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- Air Insulated Coaxial Cable 50 Ohm, Corrugated Copper, 1-5/8 in, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Jacket
- Coaxial Radiating Cable, 2650MHz, Slotted Copper Tuned Foil, 7/8 in, Black PE Jacket
- Coaxial Leaky Cable, 2650MHz, Slotted Copper Tuned Foil, 7/8 in, Non-Halogenated and Fire Retardant (LSZH) Jacket
- Coaxial RF Radiating Cable, 2650MHz, Slotted Copper Foil, 1-1/4 in, Black PE Jacket
- Coaxial RF Leaky Cable, 2650MHz, Slotted Copper Foil, 1-1/4 in, Flame Retardant Non-Corrosive (FRNC) Jacket
- Coaxial Tunnel Radiating Cable, 1000MHz, Vertical Slotted Copper Tuned Foil, 1-1/4 in, Black PE Jacket
- Coaxial Tunnel Leaky Cable, 1000MHz, Vertical Slotted Copper Tuned Foil, 1-1/4 in, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) Jacket
- Coaxial Jumper Cable SF 1/4''-50-PE, 7-16 Male Right Angle to N Male Right Angle, 1 Meter
- RF Jumper Cable SF 1/4''-50-PE, 7-16 Male Right Angle to 4.3-10 Male Right Angle, 3 Meters
- Outdoor Jumper Cable SF 1/4''-50-PE, 4.3-10 Male Right Angle to 4.3-10 Male Right Angle, 5 Meters
- RRU Jumper Cable SF 1/4''-50-PE, 4.3-10 Male Right Angle to Mini-DIN Male Right Angle, 8 Meters
- RF Cable Assembly SF 1/4''-50-PE, N Male Right Angle to N Male Right Angle, 10 Meters
- Coaxial Cable Assembly SF 1/4''-50-FRNC, 7-16 Male Straight to N Male Straight, 15 Meters
- Coaxial Jumper Cable SF 3/8''-50-PE, 7-16 Male Right Angle to N Male Right Angle, 1 Meter
- RF Jumper Cable SF 3/8''-50-PE, 7-16 Male Right Angle to 4.3-10 Male Right Angle, 3 Meters
- Outdoor Jumper Cable SF 3/8''-50-PE, 4.3-10 Male Right Angle to 4.3-10 Male Right Angle, 5 Meters
- RRU Jumper Cable SF 3/8''-50-PE, 4.3-10 Male Right Angle to Mini-DIN Male Right Angle, 8 Meters
- RF Cable Assembly SF 3/8''-50-PE, N Male Right Angle to N Male Right Angle, 10 Meters
- Coaxial Cable Assembly SF 3/8''-50-FRNC, 7-16 Male Straight to N Male Straight, 15 Meters
- Coaxial Jumper Cable SF 1/2''-50-PE, 7-16 Male Right Angle to N Male Right Angle, 1 Meter
- RF Jumper Cable SF 1/2''-50-PE, 7-16 Male Right Angle to 4.3-10 Male Right Angle, 3 Meters
- Outdoor Jumper Cable SF 1/2''-50-PE, 4.3-10 Male Right Angle to 4.3-10 Male Right Angle, 5 Meters
- RRU Jumper Cable SF 1/2''-50-PE, 4.3-10 Male Right Angle to Mini-DIN Male Right Angle, 8 Meters
- RF Cable Assembly SF 1/2''-50-PE, N Male Right Angle to NMale Right Angle, 10 Meters
- Coaxial Cable Assembly SF 1/2''-50-FRNC, 7-16 Male Straight to N Male Straight, 15 Meters
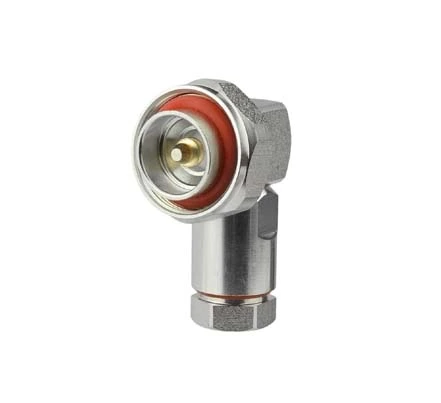
- 4.3-10 Female Connector for 1/2'' Foam Coaxial Cable
- 4.3-10 Male Connector for 1/2'' Foam Coaxial Cable
- 7/16 DIN Female Connector for 1/2'' Foam Coaxial Cable
- 7-16 DIN Male Right Angle Connector for 1/2'' Foam Coaxial Cable
- 7-16 DIN Male Connector for 1/2'' Foam Coaxial Cable
- N Female Connector for 1/2'' Coaxial Feeder Cable
- Directional In-Building Antenna, 694-3800MHz, 1-Port SISO
- Directional IBS Antenna, 694-4200MHz, 1-Port SISO
- Directional DAS Antenna, 350-2700MHz, 1-Port SISO
- Directional Panel Antenna, 617-6000MHz, 1-Port SISO
- Directional Indoor Panel Antenna, 694-3800MHz, 2-Port MIMO
- Directional 5G Panel Antenna, 694-4200MHz, 2-Port MIMO
- Low PIM Directional High Capacity Over-the-head Venue Antenna (4x4 MIMO), 1695–2700/3300-4200MHz
- Directional High Gain 4x4 MIMO Stadium Antenna, 1710-2700MHz, 30-Deg
- Directional High Capacity 2x2 MIMO Stadium Antenna, 694-960/1710-2700MHz, 30-Deg
- Directional High Gain 2x2 MIMO Stadium Antenna, 694-960/1710-2700/3300-3800MHz, 60-Deg
- Directional High Capacity 2x2 MIMO Stadium Antenna, 1710-2700/3300-4200MHz, 30-Deg
- Directional High Capacity 2x2 MIMO Venue Antenna, 1710-2700/3300-4200MHz, 30-Deg
- XXPol 1710-2700MHz×2 30°10dBi 0°Fixed Electrical Downtilt Antenna
- XXXXPol 698-960MHz×2/1710-2690MHz×2 65°/65° 10.5/12.5dBi 0°/0° Fixed Electrical Downtilt Antenna, with Combiner Integrated
- XXPol 1710-2700MHz/3400-3600MHz 30° 10dBi 0° Fixed Electrical Downtilt Antenna
- XXXXXXPol 698-960MHz×2/1710-2690MHz×4 65°/65° 10.8/12.5dBi 0°/0° Fixed Electrical Downtilt Antenna
- XXXPol 698-960MHz/1710-2690MHz×2 65°/65° 11.5/13.8dBi 0°/0° Fixed Electrical Downtilt Antenna
- XXXXPol 1695-2690MHz×2/3300-4200MHz×2 65°/65° 12.5/12.5dBi 0°/0° Fixed Electrical Downtilt Antenna
- Multiband 2-Way Low Pim Passive High Power Splitter, 694-3800MHz, 7/16 DIN Female
- Wide Band 3-Way Low Pim Passive High Power Splitter, 694-3800MHz, 7/16 DIN Female
- UHF 4-Way Low PIM Passive High Power Splitter, 694-3800MHz, 7/16 DIN Female
- Multiband 2-Way Reactive Power Splitter, 694-3800MHz, N Female
- Wide Band 3-Way Reactive Power Splitter, 694-3800MHz, N Female
- UHF 4-Way Reactive Power Splitter, 694-3800MHz, N Female
- Muilti-Band Air Directional Coupler Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 5dB, 4.3-10 Female
- Passive DAS Components Directional Coupler Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 7dB, 4.3-10 Female
- 5G Band Directional Coupler Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 10dB, 4.3-10 Female
- LTE Directional Coupler Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 13dB, 4.3-10 Female
- RF Directional Coupler Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 15dB, 4.3-10 Female
- UHF Directional Coupler Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 20dB, 4.3-10 Female
- RF Tapper Low PIM, 694-3800MHz, 4.3-10 Female, Variable Coupling Value
- Wide Band Tapper Low PIM, 694-4200MHz, 4.3-10 Female, Variable Coupling Value
- Muilti-Band Tapper Low PIM, 350-2700MHz, 4.3-10 Female, Variable Coupling Value
- 5G IBS Power Tapper, 694-3800MHz, 4.3-10 Female, Variable Coupling Value
- DAS Tapper, 694-4200MHz, 4.3-10 Female, Variable Coupling Value
- Indoor Power Tapper, 350-2700MHz, 4.3-10 Female, Variable Coupling Value
- Low PIM 2x2 High Power Hybrid Coupler, 694-3800MHz, 4.3-10 Female
- Wide Band 2x2 High Power Hybrid Coupler, 694-4200MHz, 4.3-10 Female
- Low PIM 2x2 IBS Hybrid Coupler, 350-2700MHz, 4.3-10 Female
- DAS 2x2 High Power Hybrid Coupler, 694-3800MHz, 7-16 DIN Female
- Low PIM 2x2 5G Hybrid Coupler, 694-4200MHz, 7-16 DIN Female
- LTE 2x2 High Power Hybrid Coupler, 350-2700MHz, 7-16 DIN Female
- RF Coaxial Attenuator, DC-3000MHz, 1 Watt, N Male to N Female, 3dB
- RF Attenuator, DC-4000MHz, 1 Watt, N Male to N Female, 5dB
- RF Fixed Attenuator, DC-6000MHz, 1 Watt, N Male to N Female, 10dB
- RF Coaxial Attenuator, DC-3000MHz, 2 Watt, N Male to N Female, 15dB
- RF Attenuator, DC-4000MHz, 2 Watt, N Male to N Female, 20dB
- RF Fixed Attenuator, DC-6000MHz, 2 Watt, N Male to N Female, 30dB
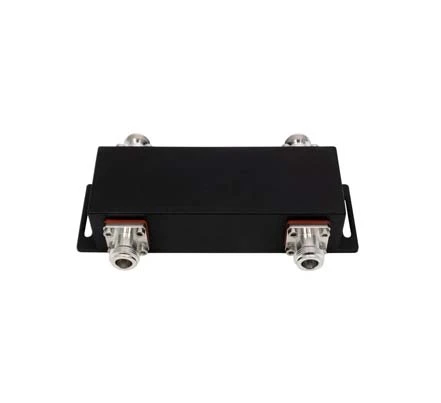
- Low PIM Hybrid Combiner 2:1 (2-Input and 1-Output), 694-960MHz, 7/16 DIN Female
- Low PIM Hybrid Combiner with Dummy Load 2:1 (2-Input and 1-Output), 1710-2170MHz, 7/16 DIN Female
- Low PIM 2 in 1 out Hybrid Combiner Integrated Termination, 694-960MHz, 7-16 DIN Female
- Low PIM Same Band Combiner 2:1 (2-Input and 1-Output), 1710-2170MHz, 4.3-10 Female
- Low PIM GSM/UMTS Combiner 2:1 (2-Input and 1-Output), 694-3800MHz, N Female
- Low PIM LTE/GSM Combiner 2:1 (2-Input and 1-Output), 694-4200MHz, N Female
- Outdoor Twin Diplexer, 1800-2100/2300-2600MHz, DC Bypass for All Ports, 4.3-10 Female
- Single Unit Diplexer, 380-960/1710-2690MHz, DC Bypass for Low-Band Port, 4.3-10 Female
- RRU Twin Diplexer, 380-2200/2300-2690MHz, DC Bypass for High-Band Port, 7/16 DIN Female
- Tower Mount Double Unit Diplexer, PCS/AWS+WCS, DC Bypass for All Ports, 4.3-10 Female
- Mobile Twin Diplexer, 2100/2600, DC Bypass for Low-Band Port, 7/16 DIN Female
- Cell Double Unit Diplexer, 698-803/824-894MHz, DC Bypass for All Ports, 7/16 DIN Female
- In-Band Diplexer, Same Band Combination, AWS A/CDEF Bands, 19'' Rack Mounting, 4.3-10 Female
- Same Band Diplexer, GSM 900/UMTS 900, Cabinet Mounting, 4.3-10 Female
- Hybrid Diplexer, ADBE/C3 Bands, 19'' Cabinet Mounting, 4.3-10 Female
- In-Band Diplexer, A CDMA/B 850/700 LTE, 19 Inch Rack Mounting, 4.3-10 Female
- Same Band Diplexer, PCS B3/B4B5, 19 Inch Cabinet Mounting, 4.3-10 Female
- In-Band Diplexer, L18/G18, Rack Installation, 7/16 DIN Female
- Outdoor Interference Mitigation Filter with Pass Band 2575-2615MHz Doule Unit
- Cellular Mobile Interference Mitigation Filter for 900 Band with Rejection 46dB in 869-894mhz Band
- Indoor Interference Mitigation Filter for 2600MHz B7 Band with Rejection 33dB in 2575-2615MHz Band
- RF Interference Mitigation Filter for 2600MHz, B38 Rejects 2500-2570&2620-2690MHz, 38db Rejection, 8-Channel
- Interference Mitigation Rf Filter for 700-750mhz Reject Guard 757-758MHz, Indoor Applicaion
- Ceramic Waveguide Filter, F0 3950MHz, Bandwidth 100MHz, 23dB Rejection, Used for GPS Systems
- Ceramic Waveguide Filter, F0 2160MHz, Bandwidth 20MHz, 42dB Rejection, Used for BD Applications
- Ceramic Waveguide Filter, F0 3350MHz, Bandwidth 100MHz, 30dB Rejection, Used for GLONASS Systems
- Ceramic Waveguide Filter, F0 2253.5MHz, Bandwidth 40MHz, 42dB Rejection, Used for 5G Equipments
- Ceramic Waveguide Duplexer, F0 1747.5MHz / 1842.5MHz, Bandwidth 75MHz, 50dB Rejection, Used for GPS and GLONASS
- Ceramic Waveguide Duplexer, F0 6675MHz / 7015MHz, Bandwidth 170MHz, 65dB Rejection, Used for GPS Antennas
- Ceramic Monoblock Duplexer, F0 897.5MHz / 942.5MHz, Bandwidth 35MHz, 50dB Rejection
- Ceramic Monoblock Duplexer, F0 1950MHz / 2140MHz, Bandwidth 60MHz, 55dB Rejection
- Ceramic Monoblock Filter, F0 2235MHz, Bandwidth 4MHz, 40dB Rejection
- Ceramic Monoblock Filter, F0 3450MHz, Bandwidth 300MHz, 30dB Rejection
- Ceramic Monoblock Filter, F0 1842.5MHz, Bandwidth 225MHz, 19dB Rejection
- Ceramic Monoblock Filter, F0 1410MHz, Bandwidth 110MHz, 40dB Rejection
- Dielectric Resonators, Center Frequency 1940MHz, Quality Factor 16000, Dielectric Constant 40
- Dielectric Resonators, Center Frequency 1975MHz, Quality Factor 14000, Dielectric Constant 40
- Dielectric Resonators, Center Frequency 1990MHz, Quality Factor 15000, Dielectric Constant 40
- Dielectric Resonators, Center Frequency 2010MHz, Quality Factor 14000, Dielectric Constant 40
- Dielectric Resonators, Center Frequency 2000MHz, Quality Factor 14000, Dielectric Constant 40
- Dielectric Resonators, Center Frequency 1940MHz, Quality Factor 14000, Dielectric Constant 40
- Solutions
- About SYMAIR
- Blog
- Download
- Support
- Contact
 EN
EN